Tools
Spatial Omics Analysis
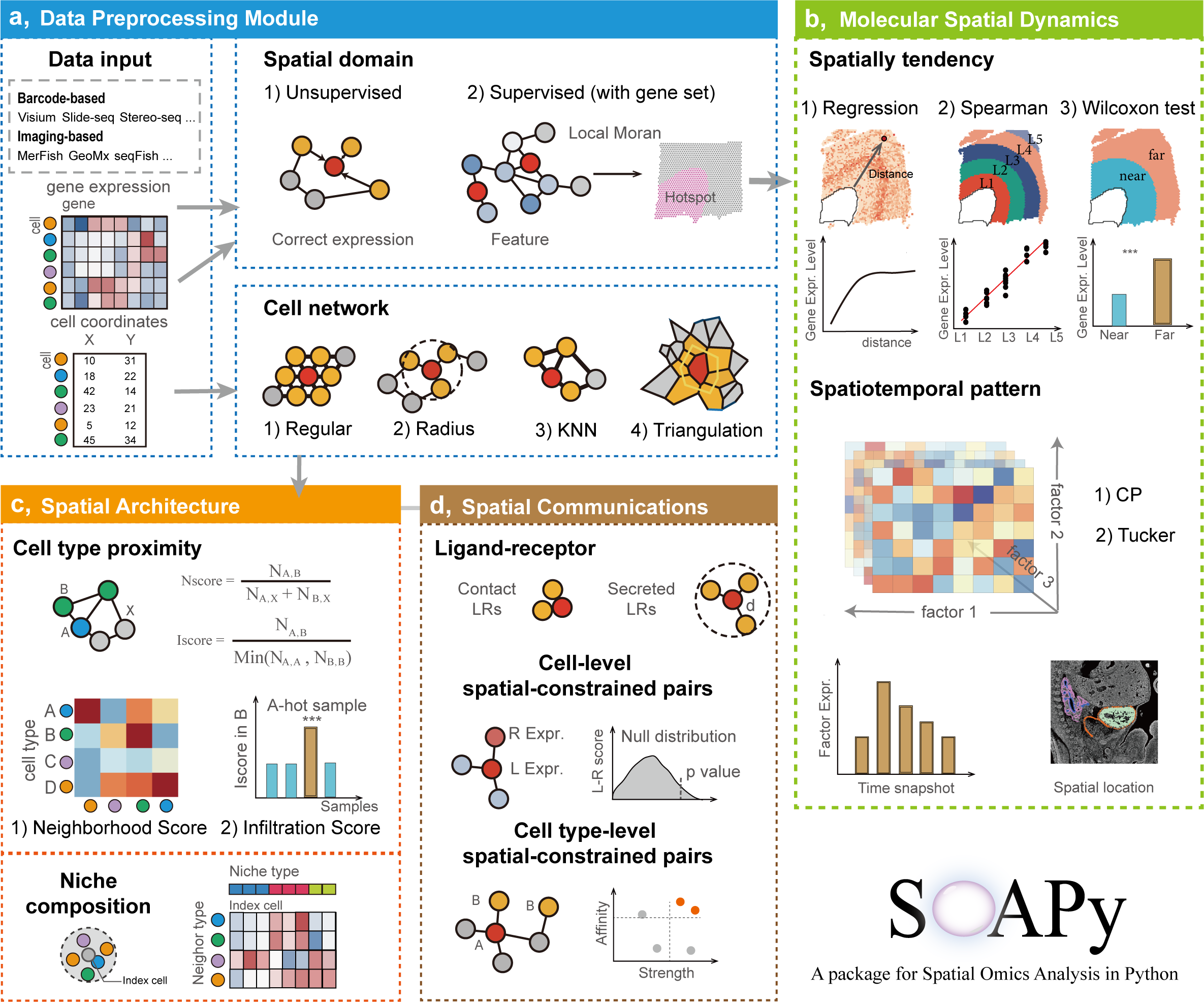
SOAPy
SOAPy is an integrated toolkit that focuses on addressing spatial heterogeneity. SOAPy contains four data preprocessing modules (“Data Import”, “spatial network”, and “Spatial Domain”), three modules for analyzing spatial expression patterns of genes (“Spatial Variation”, “Spatial Tendency”, and “Spatiotemporal Pattern”), two modules for analyzing the spatial architecture of cells (“Spatial Proximity”, “Spatial Composition”), and two module for analyzing Spatial Communication.
Cancer Precision Medicine
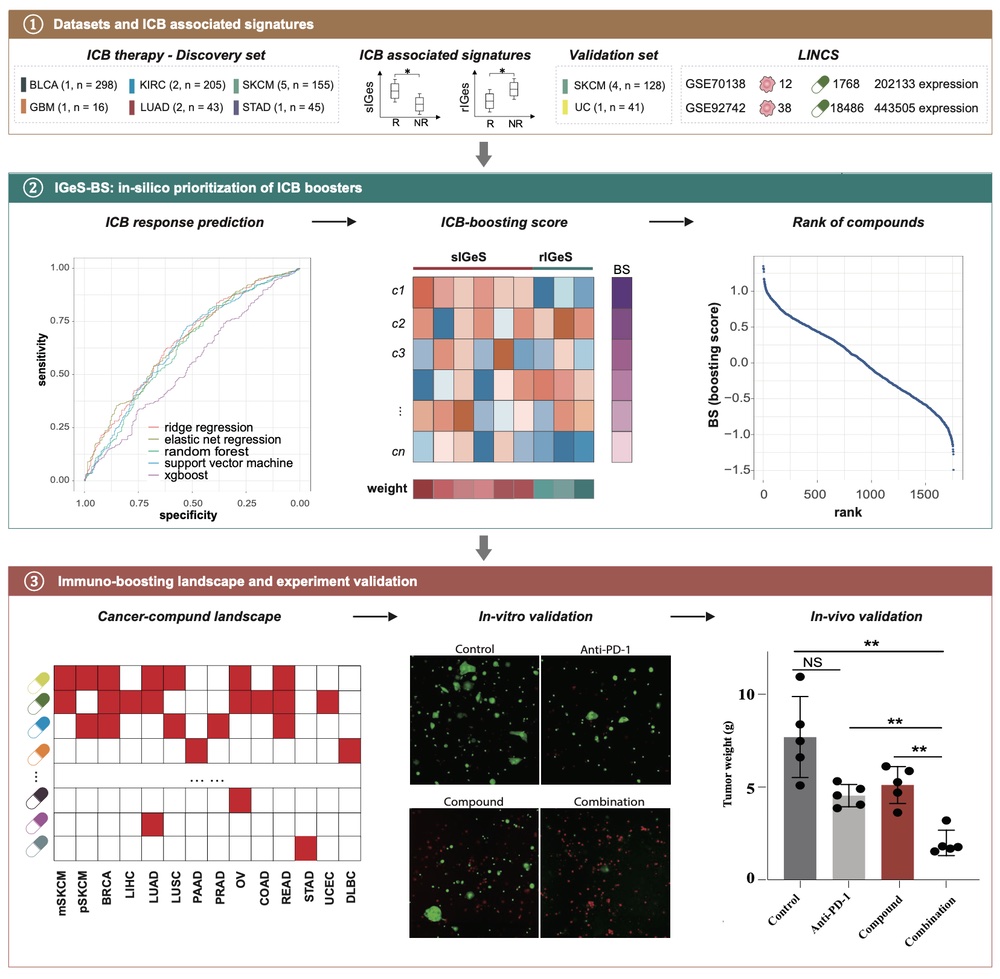
IGeS-BS
IGeS-BS is a computational framework designed to enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy by identifying compounds that can potentially overcome resistance to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) across multiple cancer types. By integrating gene expression data from cancer patients and high-throughput compound perturbation experiments, IGeS-BS constructs an immuno-boosting landscape that evaluates the potential of over 10,000 compounds. The framework employs machine learning models to prioritize compounds based on their ability to modulate immune-related gene signatures associated with ICB response. The effectiveness of IGeS-BS has been validated through computational predictions and experimental studies, demonstrating its capacity to identify promising candidates for combination therapy in cancer treatment.
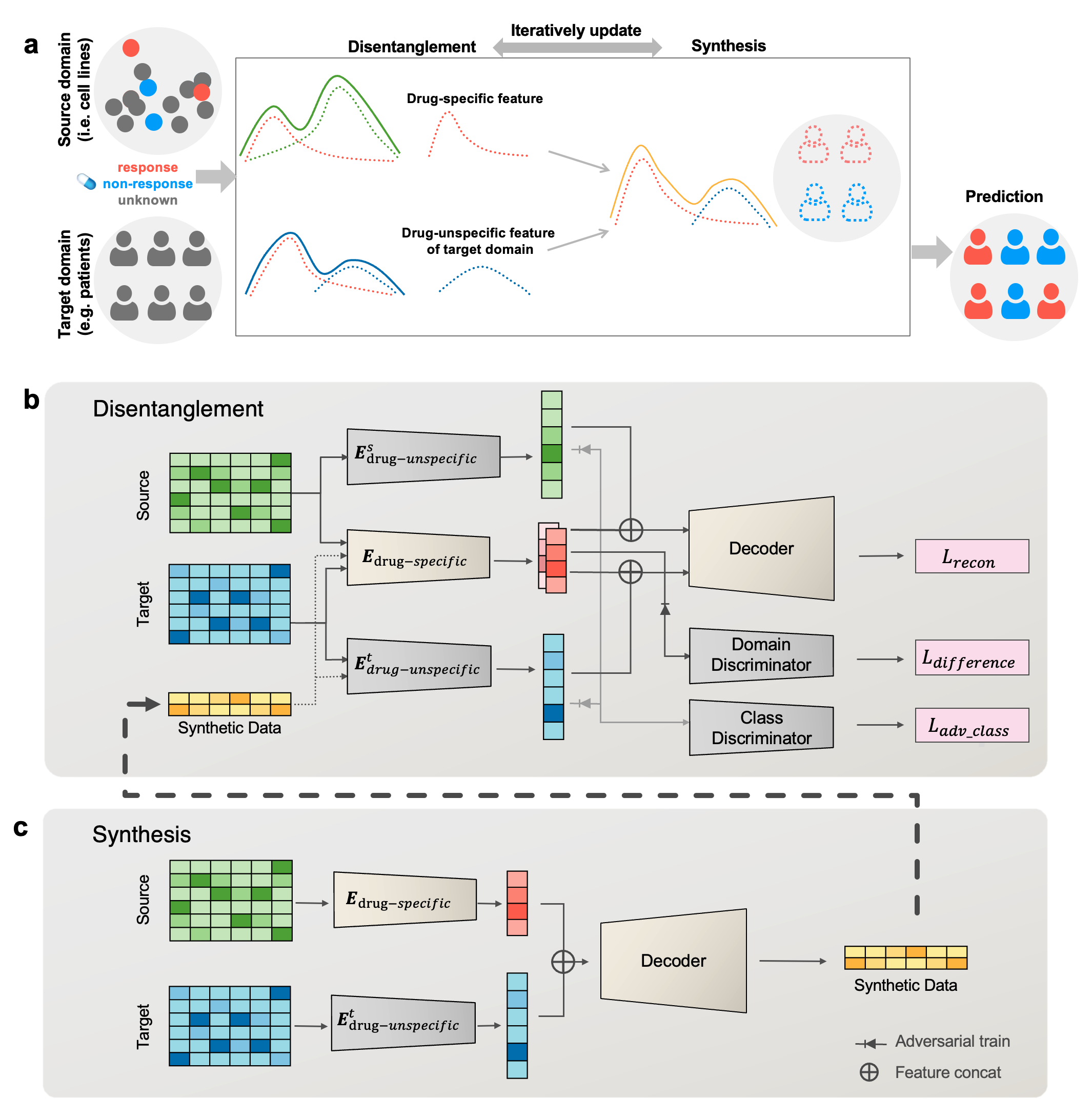
DiSyn
This is a python implementation of Disentangled Synthesis Transfer Network (DiSyn) which enhances generalizability of drug response prediction by extracting features related and unrelated to drug responses to synthesize new training samples and improve prediction accuracy of label-scarce target domains.
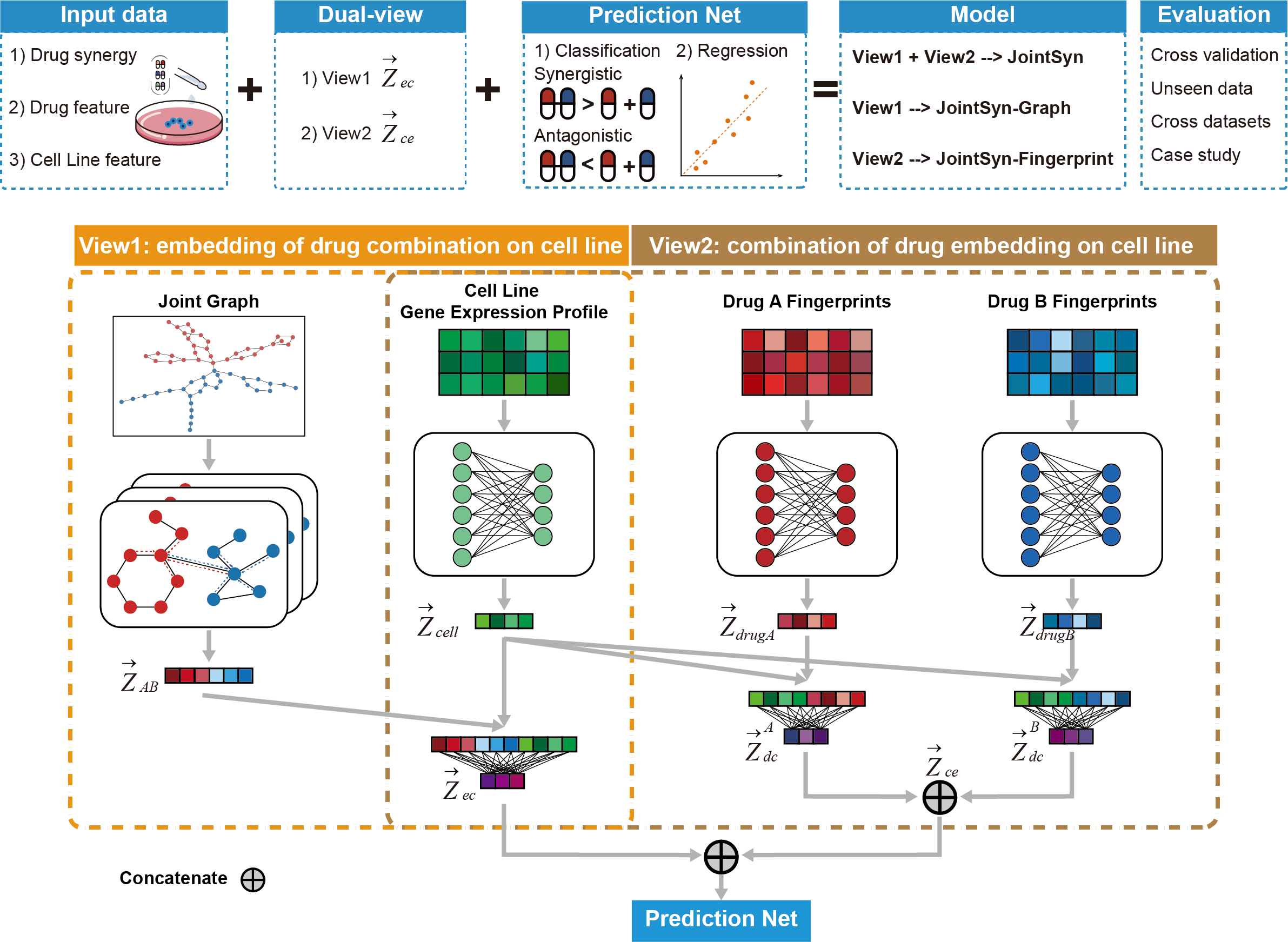
JointSyn
We have proposed JointSyn that utilizes dual-view jointly learning to predict sample-specific effects of drug combination from drug and cell features. JointSyn capture the drug synergy related features from two views. One view is the embedding of drug combination on cancer cell lines, and the other view is the combination of two drugs’ embeddings on cancer cell lines. Finally, the prediction net uses the features learned from the two views to predict the drug synergy of the drug combination on the cell line.
Single Cell Analysis
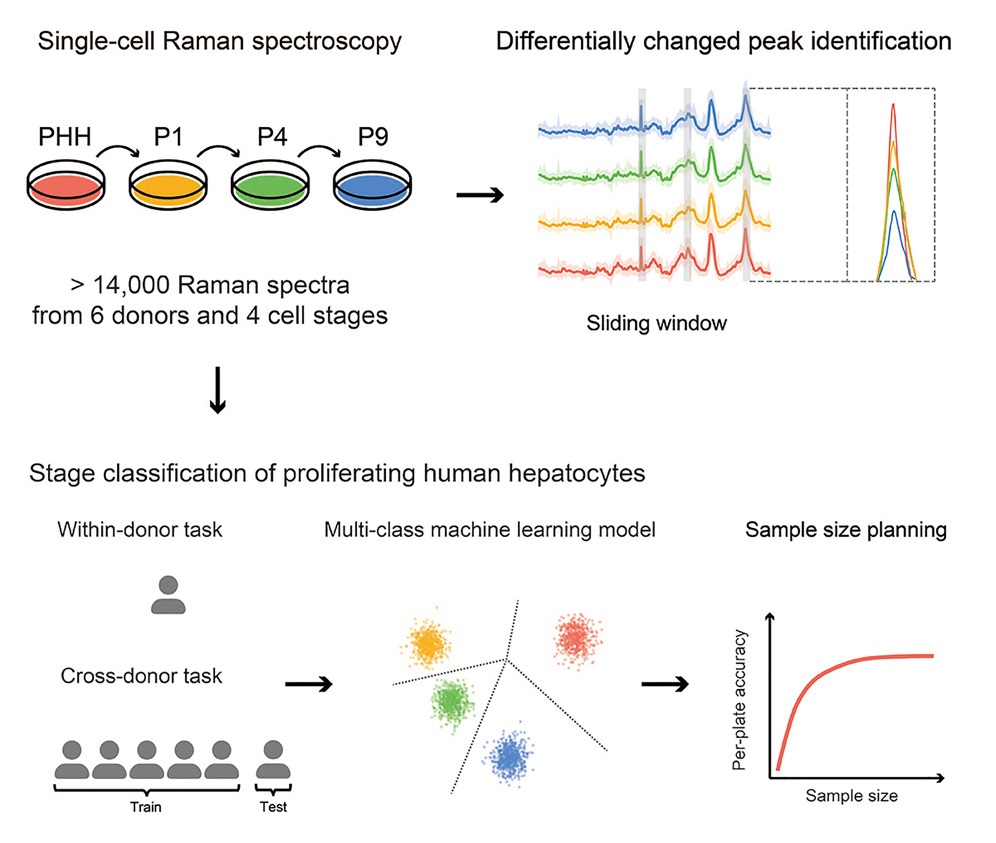
Raman Analysis
Cell therapy using proliferating human hepatocytes (ProliHHs) is an effective treatment approach for advanced liver diseases. However, rapid and accurate identification of high-quality ProliHHs from different donors is challenging due to individual heterogeneity. Here, we developed a machine learning framework to integrate single-cell Raman spectroscopy from multiple donors and identify different stages of ProliHHs. A repository of more than 14,000 Raman spectra, consisting of primary human hepatocytes (PHHs) and different passages of ProliHHs from six donors, was generated. Using a sliding window algorithm, potential biomarkers distinguishing the different cell stages were identified through differential analysis. Leveraging machine learning models, accurate classification of cell stages was achieved in both within-donor and cross-donor prediction tasks.